Carvona
compuesto químico
Carvona es un terpenoide[2] que se encuentra naturalmente en muchos aceites esenciales, especialmente en las semillas de alcaravea (Carum carvi), hierbabuena (Mentha spicata), y eneldo.[3]
| Carvona | ||
|---|---|---|
| General | ||
| Fórmula estructural |
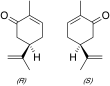 | |
| Fórmula molecular | ? | |
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 99-49-0[1] | |
| ChEBI | 38265 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL15676 | |
| ChemSpider | 21106424 | |
| PubChem | 7439 | |
| UNII | 75GK9XIA8I | |
| KEGG | C01767 | |
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 150,104465068 g/mol | |
| Índice de refracción (nD) | 1,5003 | |
Referencias
editar- ↑ Número CAS
- ↑ Simonsen, J. L. (1953). The Terpenes 1 (2nd edición). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 394-408.
- ↑ De Carvalho, C. C. C. R; Da Fonseca, M. M. R. (2006). «Carvone: Why and how should one bother to produce this terpene». Food Chemistry 95 (3): 413–422. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.01.003.
Enlaces externos
editar- Carvone En The Periodic Table of Videos (Universidad de Nottingham)